
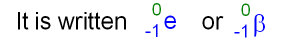
In fact, there are three ‘flavours’ of neutrino. This is a good example of science’s unique ability to predict the existence of things that have never been seen.Īnd Hey Presto! in 1956 the gamma ray signature predicted for the neutrino was actually observed for the first time. The neutrino’s existence, mass and probable behaviour had been worked out in the 1930s by Fermi and other scientists.
The power of science: finding something new that was predicted by theory This would account for the range of observed energies of beta particles and the different angles at which a nucleus could recoil. Pauli suggested that the energy liberated in beta decay was shared in a random way between the beta particle and the neutrino. The Italian physicist Enrico Fermi named it the 'neutrino', which means little neutral one in Italian. Many centimetres of lead or many meters of concrete are required to absorb high levels of gamma rays.In 1930 the Austrian physicist Wolfgang Pauli predicted that there must be another particle given off when a beta particle is produced, which is very difficult to detect.
It cannot be said that a particular thickness of a material can absorb all gamma radiation. Gamma rays are highly energetic waves and are poor at ionising other atoms or molecules. Beta radiation is a result of the ejection of charged particles from radioactive nuclei, and the charged particles are in fact electrons. Because a beta particle has a much smaller mass. Gamma rays are the most penetrating of the radiations. Just like alpha particles, beta particles interact electro- mechanically with orbital electrons (see 1.2.e). They are heavier than the alpha particles and they. Beta particles can be stopped by a few millimetres of aluminium. Definition of Beta Particles: Particles that may be found in a location in case of radiological attack. In a sheet of paper the molecules are much close together so the penetration of alpha particles is much less than in air.īeta particles travel faster than alpha particles and carry less charge (one electron compared to the 2 protons of an alpha particle) and so interact less readily with the atoms and molecules of the material through which they pass. With each collision they lose some of their energy in ionising the air molecule until eventually they give up all of their energy and are absorbed. The production of beta particles is termed beta decay.

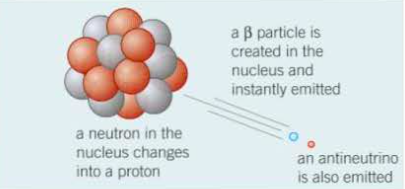
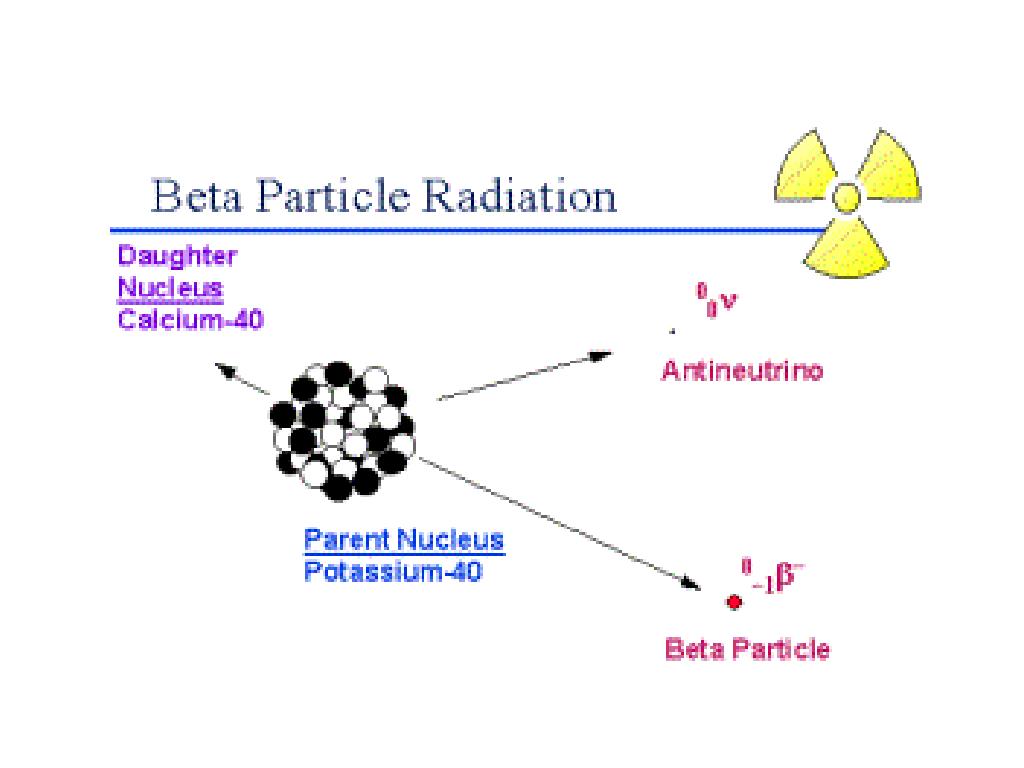
Radiation Toxicology, Ionizing and Nonionizing. Beta particles are equivalent to electrons but arise from radioactive. When an atom emits a particle, the atom's mass will not change (because there is no change in the total number of nuclear particles). The beta particle has the same mass and charge as an electron. The beta particles are a form of ionizing radiation also known as beta rays. Beta radiation () is the transmutation of a neutron into a proton and an electron (followed by the emission of the electron from the atom's nucleus: ). As alpha particles travel through air they collide with nitrogen and oxygen molecules. Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by certain fission fragments or by certain primordial radioactive nuclei such as potassium-40. Alpha particles can be absorbed by a thin sheet of paper or by a few centimetres of air.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
